Dissertations / Theses on the topic 'Space-time in RS Model'
Create a spot-on reference in APA, MLA, Chicago, Harvard, and other styles
Consult the top 50 dissertations / theses for your research on the topic 'Space-time in RS Model.'
Next to every source in the list of references, there is an 'Add to bibliography' button. Press on it, and we will generate automatically the bibliographic reference to the chosen work in the citation style you need: APA, MLA, Harvard, Chicago, Vancouver, etc.
You can also download the full text of the academic publication as pdf and read online its abstract whenever available in the metadata.
Browse dissertations / theses on a wide variety of disciplines and organise your bibliography correctly.
Langford, William P. "A space-time flow optimization model for neighborhood evacuation." Thesis, Monterey, California : Naval Postgraduate School, 2010. http://edocs.nps.edu/npspubs/scholarly/theses/2010/Mar/10Mar%5FLangford.pdf.
Full textThesis Advisor: Alderson, David L. Second Reader: Church, Richard L. "March 2010." Author(s) subject terms: Evacuation, Network, Flow Optimization, Space-Time network. Includes bibliographical references (p. 41-42). Also available in print.
Hone, David M. "Time and space resolution and mixed layer model accuracy." Monterey, California. Naval Postgraduate School, 1997. http://hdl.handle.net/10945/9080.
Full textEhlers, Ricardo Sandes. "Bayesian model discrimination for time series and state space models." Thesis, University of Surrey, 2002. http://epubs.surrey.ac.uk/843599/.
Full textMellor, Dale. "The modified turning bands (MTB) model for space-time rainfall." Thesis, University of Newcastle Upon Tyne, 1993. http://ethos.bl.uk/OrderDetails.do?uin=uk.bl.ethos.357808.
Full textGranholm, George Richard 1976. "Near-real time atmospheric density model correction using space catalog data." Thesis, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, 2000. http://hdl.handle.net/1721.1/44899.
Full textIncludes bibliographical references (p. 179-184).
Several theories have been presented in regard to creating a neutral density model that is corrected or calibrated in near-real time using data from space catalogs. These theories are usually limited to a small number of frequently tracked "calibration satellites" about which information such as mass and crosssectional area is known very accurately. This work, however, attempts to validate a methodology by which drag information from all available low-altitude space objects is used to update any given density model on a comprehensive basis. The basic update and prediction algorithms and a technique to estimate true ballistic factors are derived in detail. A full simulation capability is independently verified. The process is initially demonstrated using simulated range, azimuth, and elevation observations so that issues such as required number and types of calibration satellites, density of observations, and susceptibility to atmospheric conditions can be examined. Methods of forecasting the density correction models are also validated under different atmospheric conditions.
by George Richard Granholm.
S.M.
Mukherjee, Smarajit. "Time- and Space-resolved Heat Transfer Model for Spark-Ignition Engines." The Ohio State University, 2018. http://rave.ohiolink.edu/etdc/view?acc_num=osu1517440404339384.
Full textKotecha, Vinay. "Solitons on lattices and curved space-time." Thesis, Durham University, 2001. http://etheses.dur.ac.uk/3845/.
Full textGuadagnin, Fábio. "Identidades espaço-temporais em Terra de Areia/RS : um estudo sobre o tempo e a geografia." reponame:Biblioteca Digital de Teses e Dissertações da UFRGS, 2008. http://hdl.handle.net/10183/15274.
Full textThe use of the concept of time as a category of analysis in Geography is not as rare as we imagine, but neither is as reflexive or common as we would like it to be. Even more rare are the scientific works that include in an effective way the space-time dimension in geographical analysis. This research presents, therefore, a discussion about authors who discuss this perspective, in trying to build the concepts of space-time, temporality (matter and information transport speed) and spatial-temporal identity at the same time that tries to link them to the conceptual universe of Geography. Also, this research tries to demonstrate a possibility of effective use of these concepts in the analysis of a specific portion of space. The experimental field work was developed in the city of Terra de Areia, in the northern coast of Rio Grande do Sul/Brazil, where several flows with different speeds live closely, generating temporal conflicts manifested in habits, gestures and feelings of the inhabitants of the town.
Boguta, Maria. "A New Space-Time Model for Interacting Agents in the Financial Market." Thesis, Halmstad University, School of Information Science, Computer and Electrical Engineering (IDE), 2009. http://urn.kb.se/resolve?urn=urn:nbn:se:hh:diva-3180.
Full textIn this thesis we present a new space-time model of interacting agents in the financial market. It is a combination of the Curie-Weiss model and a model introduced by Järpe. We investigate properties such as the critical temperature and magnetization of the system. The distribution of the Hamiltonian function is obtained and a hypothesis test of independence is derived. The results are illustrated in an example based on real data.
Parashkevov, Atanas. "Advances in space and time efficient model checking of finite state systems." Title page, contents and abstract only, 2002. http://web4.library.adelaide.edu.au/theses/09PH/09php223.pdf.
Full textBhattacharyya, Mainak. "A model reduction approach in space and time for fatigue damage simulation." Thesis, Université Paris-Saclay (ComUE), 2018. http://www.theses.fr/2018SACLN019/document.
Full textThe motivation of the research project is to predict the life time of mechanical components that are subjected to cyclic fatigue phenomena. The idea herein is to develop an innovative numerical scheme to predict failure of structures under such loading. The model is based on classical continuum damage mechanics introducing internal variables which describe the damage evolution. The challenge lies in the treatment of large number of load cycles for the life time prediction, particularly the residual life time for existing structures.Traditional approaches for fatigue analysis are based on phenomenological methods and deal with the usage of empirical relations. Such methods consider simplistic approximations and are unable to take into account complex geometries, and complicated loadings which occur in real-life engineering problems. A thermodynamically consistent continuum-based approach is therefore used for modelling the fatigue behaviour. This allows to consider complicated geometries and loads quite efficiently and the deterioration of the material properties due to fatigue can be quantified using internal variables. However, this approach can be computationally expensive and hence sophisticated numerical frameworks should be used.The numerical strategy used in this project is different when compared to regular time incremental schemes used for solving elasto-(visco)plastic-damage problems in continuum framework. This numerical strategy is called Large Time Increment (LATIN) method, which is a non-incremental method and builds the solution iteratively for the complete space-time domain. An important feature of the LATIN method is to incorporate an on-the-fly model reduction strategy to reduce drastically the numerical cost. Proper generalised decomposition (PGD), being a priori a model reduction strategy, separates the quantities of interest with respect to space and time, and computes iteratively the spatial and temporal approximations. LATIN-PGD framework has been effectively used over the years to solve elasto-(visco)plastic problems. Herein, the first effort is to solve continuum damage problems using LATIN-PGD techniques. Although, usage of PGD reduces the numerical cost, the benefit is not enough to solve problems involving large number of load cycles and computational time can be severely high, making simulations of fatigue problems infeasible. This can be overcome by using a multi-time scale approach, that takes into account the rapid evolution of the quantities of interest within a load cycle and their slow evolution along the load cycles. A finite element like description with respect to time is proposed, where the whole time domain is discretised into time elements, and only the nodal cycles, which form the boundary of the time elements, are calculated using LATIN-PGD technique. Thereby, classical shape functions are used to interpolate within the time element. This two-scale LATIN-PGD strategy enables the reduction of the computational cost remarkably, and can be used to simulate damage evolution in a structure under fatigue loading for a very large number of cycles
Karunaratne, Senani Bandara. "Modelling soil organic Carbon in space and time." Thesis, The University of Sydney, 2014. http://hdl.handle.net/2123/10289.
Full textSilveira, Emerson Lizandro Dias. "TRANSFORMAÇÕES NA ORGANIZAÇÃO ESPACIAL DO MUNICÍPIO DE RIO PARDO RS." Universidade Federal de Santa Maria, 2009. http://repositorio.ufsm.br/handle/1/9308.
Full textA presente dissertação busca compreender o processo de organização espacial do município de Rio Pardo(RS) a partir das transformações territoriais em distintos momentos históricos, desde sua fundação, até a ação contemporânea dos novos atores econômicos e políticos que se articulam no município em estudo. Os objetivos específicos buscam: (a) caracterizar os diferentes marcos de estagnação econômica sofridos pelo município ao longo do tempo;(b) apreender os efeitos do processo de globalização na economia gaúcha e no município de Rio Pardo, o qual é responsável por transformações nas atividades agrícolas tradicionais; (c) compreender o papel do estado, das políticas públicas e das empresas privadas em Rio Pardo, os quais redefinem novas dinâmicas e funcionalidades espaciais; (d) verificar como as novas dinâmicas repercutem nos setores econômicos, sociais e na cultura, reorganizando o espaço do município em estudo. A metodologia de pesquisa embasa-se no método dialético, buscando compreender, ao longo do tempo, os diferentes períodos históricos de desenvolvimento e estagnação que Rio Pardo sofreu, bem como suas consequências sócioespaciais. A pesquisa foi realizada a partir da coleta de dados primários, tais como entrevistas semiestruturadas e abertas e registros fotográficos através de trabalho de campo. Os dados secundários foram extraídos de publicações do Instituto Brasileiro de Geografia e Estatística, da FEE (Fundação de Economia e Estatística) e Emater. A organização espacial do município de Rio Pardo é resultado de um processo histórico que confunde-se com a própria história do Rio Grande do Sul. Em função de diversas transformações de ordem econômica, política, social e cultural sofridas pelo território gaúcho, a cidade foi perdendo importância no cenário econômico e político, pois manteve sua base produtiva assentada na agropecuária tradicional, tornando-se um espaço estagnado, sem dinamismo econômico capaz de atrair investimentos e de se desenvolver. Atualmente, em função das novas lógicas capitalistas no Rio Grande do Sul e de diferentes políticas públicas desenvolvimentistas, percebem-se novas dinâmicas que se desenham no espaço e provocam mudanças econômicas, políticas, culturais e técnicas em Rio Pardo.
Demel, Samuel Seth. "Modeling and computations of multivariate datasets in space and time." Diss., Kansas State University, 2013. http://hdl.handle.net/2097/15578.
Full textDepartment of Statistics
Juan Du
Spatio-temporal and/or multivariate dependence naturally occur in datasets obtained in various disciplines; such as atmospheric sciences, meteorology, engineering and agriculture. There is a great deal of need to effectively model the complex dependence and correlated structure exhibited in these datasets. For this purpose, this dissertation studies methods and application of the spatio-temporal modeling and multivariate computation. First, a collection of spatio-temporal functions is proposed to model spatio-temporal processes which are continuous in space and discrete over time. Theoretically, we derived the necessary and sufficient conditions to ensure the model validity. On the other hand, the possibility of taking the advantage of well-established time series and spatial statistics tools makes it relatively easy to identify and fit the proposed model in practice. The spatio-temporal models with some ARMA discrete temporal margin are fitted to Kansas precipitation and Irish wind datasets for estimation or prediction, and compared with some general existing parametric models in terms of likelihood and mean squared prediction error. Second, to deal with the immense computational burden of statistical inference for multi- ple attributes recorded at a large number of locations, we develop Wendland-type compactly supported covariance matrix function models and propose multivariate covariance tapering technique with those functions for computation reduction. Simulation studies and US tem- perature data are used to illustrate applications of the proposed multivariate tapering and computational gain in spatial cokriging. Finally, to study the impact of weather change on corn yield in Kansas, we develop a spatial functional linear regression model accounting for the fact that weather data were recorded daily or hourly as opposed to the yearly crop yield data and the underlying spatial autocorrelation. The parameter function is estimated under the functional data analysis framework and its characteristics are investigated to show the influential factor and critical period of weather change dictating crop yield during the growing season.
De, Swarup. "A Bayesian Space-Time Dynamic Linear Model for Radioactivity Deposition after a Nuclear Accident." Thesis, Open University, 2009. http://ethos.bl.uk/OrderDetails.do?uin=uk.bl.ethos.503619.
Full textYang, Yong. "Simulation the transmission of airborne infectious disease by individual space-time activity-based model." Thesis, University of Southampton, 2007. http://ethos.bl.uk/OrderDetails.do?uin=uk.bl.ethos.440623.
Full textBengtsson, Thomas. "Time series discrimination, signal comparison testing, and model selection in the state-space framework /." free to MU campus, to others for purchase, 2000. http://wwwlib.umi.com/cr/mo/fullcit?p9974611.
Full textZhang, Xiaohui. "Integration of a stochastic space-time rainfall model and distributed hydrologic simulation with GIS." Diss., The University of Arizona, 1997. http://hdl.handle.net/10150/282409.
Full textLUPPI, MASSIMILIANO. "Analysis of species distribution in time and space for wildlife conservation." Doctoral thesis, Università degli Studi di Milano-Bicocca, 2016. http://hdl.handle.net/10281/138011.
Full textThe general aim of my thesis is the identification and the application of appropriate modelling approaches, concerning wildlife conservation, ranging from the analysis of species distribution and population trends, to ecological connectivity and the habitat management, within area affected by different human impact or land abandonment. The specific objectives of the project are developed in the following case studies. Species distribution modelling and population trends of breeding birds in agro-ecosystems: the case of Lombardy (Italy) We analysed the population trends and distributions of breeding birds in Lombardy, focusing on agro-ecosystem species. We collected data following a stratified random sampling design by means of point counts technique. Species distribution and abundance were estimated using generalised additive models (GAMs). We assessed the mean annual variation rate for 19 species, between 1992 and 2015, applying the discrete population growth model. Over the whole period, as extreme values at regional scale, the Skylark showed a significant population decline, losing about the 90% of initial population, while the Common Wood Pigeon presented a fourfold increase. Long- and medium-term changes in the altitudinal distribution of breeding birds in the Italian Alps We used the response curve shape method to investigate changes in altitudinal distributions of breeding birds over a long-term period (1982-2015) in the central Alps, and over a medium-term period (2006-2015) to compare the dynamics occurred in the central and western Alps. During the long-term period, all species exhibited changes in at least one part of their altitudinal distribution. Most woodland species expanded towards higher and lower altitudes, probably stimulated by forest regrowth and/or temperature increase. Almost all alpine grassland species retracted the lower portion of their altitudinal range, moving towards the summit. During the medium-term period, both alpine areas showed an increase in species moving downwards, which confirms the relevance of this apparently contrasting pattern. Ecological connectivity assessment in a strongly structured fire salamander (Salamandra salamandra) population The aim of this study was to assess the ecological connectivity of fire salamander populations by means of a landscape genetic approach. The degree of isolation between populations could be evaluated measuring their genetic distances, which depend on the respective geographic (isolation by distance, IBD) and/or ecological (isolation by resistance, IBR) distances. The latter were calculated using the circuit theory, applied to habitat suitability maps. Mantel tests between distance matrices highlighted how the genetic distance in Prealpine and Eastern foothill lowland populations was related to geographic distance, while it was explained by the ecological distance, in fragmented populations of Western foothill lowland. Local and landscape drivers of butterfly richness and abundance in a human-dominated area We analysed the effects of habitat variables (local scale) and land-use variables (local and landscape scale) on butterfly richness and abundance using GAMM models. The local scale habitat models showed that the abundance of nectar plants is the most important driver of species richness and abundance. This result, together with the negative effect of the number of cuts of meadows on butterfly abundance and the positive effect of the taller herbaceous layer, highlighted the importance to adopt correct management measures in semi-natural habitats. Considering the land-use models an increase of artificial surfaces at the landscape scale leaded to a decrease of the positive effect played by meadows at local scale, which is one of the primary habitats for butterflies.
Frederick, Lorinda A. "Deterrence and space-based missile defense /." Maxwell AFB, Ala. : School of Advanced Air and Space Studies, 2008. https://www.afresearch.org/skins/rims/display.aspx?moduleid=be0e99f3-fc56-4ccb-8dfe-670c0822a153&mode=user&action=downloadpaper&objectid=2c4a986d-2074-4005-b963-1b697e841d8c&rs=PublishedSearch.
Full textSeidl, Christoph. "Integrated Management of Variability in Space and Time in Software Families." Doctoral thesis, Saechsische Landesbibliothek- Staats- und Universitaetsbibliothek Dresden, 2017. http://nbn-resolving.de/urn:nbn:de:bsz:14-qucosa-218036.
Full textLe, Coënt Adrien. "Guaranteed control synthesis for switched space-time dynamical systems." Thesis, Université Paris-Saclay (ComUE), 2017. http://www.theses.fr/2017SACLN039/document.
Full textIn this thesis, we focus on switched control systems described by partial differential equations, and investigate the issues of guaranteed control of such systems using state-space decomposition methods. The use of state-space decomposition methods requires model order reduction, control of the different sources of error for quantities of interest, and measure of uncertainties on the states and parameters of the system. We are considering using set-based computation methods, in association with model order reduction techniques, along with the use of state-observers for on-line estimation of the system
CARLOS, MAURO LAWALL EVARISTO. "A STATISTICAL INVESTIGATION ON TIME SERIES MODELS FOR COUNT DATA: GARMA MODEL AND THE STATE SPACE POISSON GAMMA MODEL." PONTIFÍCIA UNIVERSIDADE CATÓLICA DO RIO DE JANEIRO, 2006. http://www.maxwell.vrac.puc-rio.br/Busca_etds.php?strSecao=resultado&nrSeq=10009@1.
Full textO presente trabalho tem como objetivo principal investigar por meio de simulação Monte Carlo algumas propriedades estatísticas dos modelos GARMA (Generalized Autoregressive Moving Average) para séries temporais de dados de contagem. Os modelos GARMA são uma extensão dos Modelos Lineares Generalizados de McCullagh e Nelder para situações de dados dependentes, caracterizando-se pela adição de um termo extra ao preditor linear, o qual passa a incorporar termos autoregressivos (AR) e de médias móveis (MA). As propriedades estatísticas investigadas foram às condições de estacionariedade dos modelos GARMA e os critérios de identificação da ordem (p,q) dos polinômios AR e MA que definem o modelo. Os resultados encontrados indicam que os critérios AIC BIC e Hannan-Quin utilizados foram razoavelmente eficazes na identificação da ordem dos modelos e que as condições de estacionariedade estabelecidas empiricamente em termo de restrições no espaço paramétrico são bastante complexas exigindo um estudo mais detalhado. Como objetivo secundário testamos os modelo GARMA em séries reais, ajustando os modelos GARMA- Poissson e GARMA-Binomial Negativa ao número de caso de poliomielite nos EUA e ao número de infartos do miocárdio no município do Rio de Janeiro. Os resultados indicam que os modelos foram capazes de explicar, de forma econômica, a variação destas séries.
The main objective of this dissertation is to investigate, using Monte Carlo simulations, some statistical properties of GARMA (Generalized Autoregressive Moving Average ) models for time series of count data. GARMA models are extensions of the Generalized Linear Models to dependent data, in which autoregressive (AR) and/or moving average (MA) terms are incorporated into the linear predictor. The statistical properties targeted in our investigation were the model stationarity conditions and the identification criteria for selection of model orders, the lag structure (p,q) associated with the AR and MA terms. Our results suggest that AIC, BIC and Hann-Quinn criteria worked relatively well in identifying the model order, and that the conditions for stationarity established empirically in terms of parameter space restrictions were not totally conclusive, requiring further investigation. As a secondary objective we tested the model against real data, by fitting both a GARMA-Poisson and a GARMA-Negative Binomial to the series of number of cases of poliomyelitis on the US and the number of heart-attacks in Rio de Janeiro city. The results we found indicate that these models were able to explain, in a parsimonious way, the variation of both series.
Acheson, Emily. "Predicting Disease Vector Distributions Through Space and Time Using Environmental and Vector Control Data." Thesis, Université d'Ottawa / University of Ottawa, 2015. http://hdl.handle.net/10393/32797.
Full textBrien, Jeffrey. "Mixed Emotions: Can People Feel Happy and Sad at the Same Time?" Thesis, Boston College, 2003. http://hdl.handle.net/2345/426.
Full textI studied whether or not people can feel happy and sad at the same moment in time. Participants used a computerized procedure to continuously rate their feelings as they viewed backwardly masked faces designed to elicit pleasant, unpleasant, or mixed feelings. The backward masking procedure and grid were poorly calibrated as participants found all conditions to be unpleasant. Evidence is presented that participants did not perceive the mask faces as neutral. Directions for future studies are discussed
Thesis (BA) — Boston College, 2003
Submitted to: Boston College. College of Arts and Sciences
Discipline: Psychology
Discipline: College Honors Program
Manikku, Acharige Niranjan Sanjeeva Wimalathunge. "Space-time modelling of soil moisture: prediction and forecasting for improved agricultural management." Thesis, The University of Sydney, 2019. http://hdl.handle.net/2123/21122.
Full textBjörnberg, Jakob Erik. "Graphical representations of Ising and Potts models stochastic geometry of the quantum Ising model and the space-time Potts model /." Stockholm : Skolan för teknikvetenskap, Kungliga Tekniska högskolan, 2009. http://urn.kb.se/resolve?urn=urn:nbn:se:kth:diva-11267.
Full textBjörnberg, Jakob Erik. "Graphical representations of Ising and Potts models : Stochastic geometry of the quantum Ising model and the space-time Potts model." Doctoral thesis, KTH, Matematik (Inst.), 2009. http://urn.kb.se/resolve?urn=urn:nbn:se:kth:diva-11267.
Full text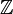 . In Chapter 3 we develop an alternative graphical representation of the quantum Ising model, called the random-parity representation. This representation is based on the random-current representation of the classical Ising model, and allows us to study in much greater detail the phase transition and critical behaviour. A major aim of this chapter is to prove sharpness of the phase transition in the quantum Ising model—a central issue in the theory— and to establish bounds on some critical exponents. We address these issues by using the random-parity representation to establish certain differential inequalities, integration of which gives the results. In Chapter 4 we explore some consequences and possible extensions of the results established in Chapters 2 and 3. For example, we determine the critical point for the quantum Ising model in
. In Chapter 3 we develop an alternative graphical representation of the quantum Ising model, called the random-parity representation. This representation is based on the random-current representation of the classical Ising model, and allows us to study in much greater detail the phase transition and critical behaviour. A major aim of this chapter is to prove sharpness of the phase transition in the quantum Ising model—a central issue in the theory— and to establish bounds on some critical exponents. We address these issues by using the random-parity representation to establish certain differential inequalities, integration of which gives the results. In Chapter 4 we explore some consequences and possible extensions of the results established in Chapters 2 and 3. For example, we determine the critical point for the quantum Ising model in 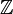 and in ‘star-like’ geometries.
and in ‘star-like’ geometries.HTML clipboard Statistisk fysik syftar till att förklara ett materials makroskopiska egenskaper i termer av dess mikroskopiska struktur. En särskilt intressant egenskap är är fenomenet fasövergång, det vill säga en plötslig förändring i de makroskopiska egenskaperna när externa förutsättningar varieras. Två modeller är särskilt intressanta för en matematiker, nämligen Ising-modellen av en magnet och perkolationsmodellen av ett poröst material. Dessa två modeller sammanförs av den så-kallade fk-modellen, en slumpgrafsmodell som först studerades av Fortuin och Kasteleyn på 1970-talet. fk-modellen har sedermera visat sig vara extremt användbar för att bevisa viktiga resultat om Ising-modellen och liknande modeller. I den här avhandlingen studeras den motsvarande grafiska strukturen hos två näraliggande modeller. Den första av dessa är den kvantteoretiska Isingmodellen med transverst fält, vilken är en utveckling av den klassiska Isingmodellen och först studerades av Lieb, Schultz och Mattis på 1960-talet. Den andra modellen är rumtid-perkolation, som är nära besläktad med kontaktmodellen av infektionsspridning. I Kapitel 2 definieras rumtid-fk-modellen, och flera probabilistiska verktyg utforskas för att studera dess grundläggande egenskaper. Vi möter rumtid-Potts-modellen, som uppenbarar sig som en naturlig generalisering av den kvantteoretiska Ising-modellen. De viktigaste egenskaperna hos fasövergången i dessa modeller behandlas i detta kapitel, exempelvis det faktum att det i fk-modellen finns högst en obegränsad komponent, samt den undre gräns för det kritiska värdet som detta innebär. I Kapitel 3 utvecklas en alternativ grafisk framställning av den kvantteoretiska Ising-modellen, den så-kallade slumpparitetsframställningen. Denna är baserad på slumpflödesframställningen av den klassiska Ising-modellen, och är ett verktyg som låter oss studera fasövergången och gränsbeteendet mycket närmare. Huvudsyftet med detta kapitel är att bevisa att fasövergången är skarp—en central egenskap—samt att fastslå olikheter för vissa kritiska exponenter. Metoden består i att använda slumpparitetsframställningen för att härleda vissa differentialolikheter, vilka sedan kan integreras för att lägga fast att gränsen är skarp. I Kapitel 4 utforskas några konsekvenser, samt möjliga vidareutvecklingar, av resultaten i de tidigare kapitlen. Exempelvis bestäms det kritiska värdet hos den kvantteoretiska Ising-modellen på
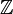 , samt i ‘stjärnliknankde’ geometrier.
, samt i ‘stjärnliknankde’ geometrier.QC 20100705
Björnberg, Jakob Erik. "Graphical representations of Ising and Potts models : stochastic geometry of the quantum Ising model and the space-time Potts model." Thesis, University of Cambridge, 2010. https://www.repository.cam.ac.uk/handle/1810/224774.
Full textBitto, Angela, and Sylvia Frühwirth-Schnatter. "Achieving shrinkage in a time-varying parameter model framework." Elsevier, 2019. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jeconom.2018.11.006.
Full textSilva, Rogério Marques. "ESPAÇO E TEMPO NAS MINAS DO CAMAQUÃ EM CAÇAPAVA DO SUL/RS." Universidade Federal de Santa Maria, 2008. http://repositorio.ufsm.br/handle/1/9285.
Full textAtualmente, vive-se uma realidade onde a questão econômica possui grande importância. Diante disto, o espaço geográfico, produto das transformações sócio-econômicas ao longo do tempo, pode servir de importante foco de pesquisa no que confere a tais tendências. Neste contexto, apresenta-se as Minas do Camaquã, no município de Caçapava do Sul, no Rio Grande do Sul, um conjunto de vilas operárias formadas ao longo de 130 anos de exploração de cobre, como objeto de estudo, cujo objetivo se é a tentativa do entendimento das transformações espaciais ao longo do processo de extração de cobre verificando-se ainda as tendências futuras para este espaço. A metodologia de pesquisa parte de uma visão dialética, onde inicialmente realizou-se o levantamento da história do local a fim de se estudar as diferentes conformações espaciais ao longo da produção de cobre. Posteriormente, buscou-se através de entrevistas qualificadas e aplicação de questionários o entendimento da dinâmica espacial durante e após o término da atividade de mineração, verificando-se ainda as prováveis tendências espaciais para os próximos anos. A partir de 1942, a Companhia Brasileira do cobre - CBC passou a extrair cobre nesta região. Deste momento em diante, a paisagem local passaria a comportar uma estrutura urbana formada por uma área industrial e um conjunto de sete vilas além de clubes, praças, hospitais entre outros. Após 50 anos, a profundidade das reservas de cobre, aliada aos baixos preços do minério e a política brasileira de privatizações, foram os motivos que levaram o encerramento das atividades no ano de 1996. Deste momento em diante, toda a estrutura dos tempos de mineração foi abandonada. De aproximadamente 5000 moradores, restaram cerca de 400. Vilas inteiras foram desativadas. Prédios foram demolidos. Após 12 anos do término das atividades, pode-se verificar que existem algumas idéias sendo trabalhadas, porém ainda muito longe de sanar as necessidades da localidade. Sucessivos governos municipais e seu descaso com o local fazem hoje das Minas do Camaquã, um espaço pós-industrial cujas especificidades guardam semelhanças a muitas áreas degradadas, como cidades ferroviárias desativadas e antigas bases militares, no que confere à posição desprivilegiada dentro do processo produtivo. A volta da mineração diante dos atuais estudos da geologia da região e a atividade turística devido as belas paisagens desta região, surgem como possibilidades de dinamizar a economia local.
Nail, Amy Jeanette. "Quantifying local creation and regional transport using a hierarchical space-time model of ozone as a function of observed NOx, a latent space-time VOC process, emissions, and meteorology." NCSU, 2007. http://www.lib.ncsu.edu/theses/available/etd-08092007-123658/.
Full textTang, Fan. "Structural time series clustering, modeling, and forecasting in the state-space framework." Diss., University of Iowa, 2015. https://ir.uiowa.edu/etd/6002.
Full textWanzenböck, Iris, and Philipp Piribauer. "R&D networks and regional knowledge production in Europe. Evidence from a space-time model." WU Vienna University of Economics and Business, 2015. http://epub.wu.ac.at/4652/1/wp207.pdf.
Full textSeries: Department of Economics Working Paper Series
ESPINOZA, SERGIO EDUARDO CONTRERAS. "STATE SPACE MODEL FOR TIME SERIES WITH BIVARIATE POISSON DISTRIBUTION: AN APPLICATION OF DURBIN-KOOPMAN METODOLOGY." PONTIFÍCIA UNIVERSIDADE CATÓLICA DO RIO DE JANEIRO, 2004. http://www.maxwell.vrac.puc-rio.br/Busca_etds.php?strSecao=resultado&nrSeq=5470@1.
Full textORGANIZAÇÕES DOS ESTADOS AMERICANOS
UNIVERSIDAD DEL BÍO-BÍO
Nesta tese, consideramos um modelo de espaço de estado bivariado para dados de contagem. A abordagem usada para resolver integrais não- analíticas que se apresentam no modelo é uma natural extensão da metodologia proposta por Durbin & Koopman - (DK), no sentido de que o Modelo Gaussiano Aproximador deve possuir algumas matrizes de covariâncias diagonais. Esta modificação traz a vantagem de viabilizar o uso do tratamento univariado para séries multivariadas com as recursões de Kalman, o qual, como se sabe, é mais eficiente do que o tratamento usual e facilita o uso de inicializações exatas destas mesmas recursões. O vetor de estado do modelo proposto é definido usando-se abordagem estrutural, onde os elementos do vetor de estado têm interpretação direta como tendência e sazonalidade. Apresentamos exemplos simulados e reais para ilustrar o modelo.
In this thesis we consider a state space model for bivariate observations of count data. The approach used to solve the non analytical integrals that appears as the solution of the resulting non-Gaussian filter is a natural extension of the methodology advocated by Durbin and Koopman (DK). In our approach the aproximated Gaussian Model (AGM), has a diagonal Covariance matrix, while in the original DK, this is a full matrix. This modification make it possible to use univariate Kalman recursoes to construct the AGM, resulting in a computationally more efficient solution for the estimation of a Bivariate Poisson model. This also facilitates the use of exact initialization of those recursions. The state vector is specified using the structural approach, where the state elements are components which have direct interpretation, such as trend and seasonals. In our bivariate set up the dependence between the bivariate vector of time series is accomplished by use of common components which drive both series. We present both simulation and real life examples illustrating the use of our model.
Roelly, Sylvie, and Michel Sortais. "Space-time asymptotics of an infinite-dimensional diffusion having a long- range memory." Universität Potsdam, 2004. http://opus.kobv.de/ubp/volltexte/2006/670/.
Full textPasquali, Flavia. "State space models for the analysis and forecasting of climatic time series." Master's thesis, Alma Mater Studiorum - Università di Bologna, 2021. http://amslaurea.unibo.it/23081/.
Full textValenti, Eduardo da Silva. "Modelo cartográfico digital temático para simulação e previsão de inundações no município de Porto Alegre - RS." reponame:Biblioteca Digital de Teses e Dissertações da UFRGS, 2010. http://hdl.handle.net/10183/28477.
Full textNatural disasters have always been part of the human lives, but in recent years due to growth of large urban centers, the difficulty of implementation and compliance of environmental preservation policies and increasing climate change, natural disasters are becoming common, and in the particular case of this study the damage caused by floods have affected populations beds near the water resources, causing material damage, deaths, disappearances, flagellates and homeless. To better understand the behavior of these extreme events and increase safety avoiding the lives loss and minimizing the economic losses that arise from these disasters, it is necessary to study the possible affected areas identifying the risk sites and quantifying the criticality of an event of great magnitude. Based on studies of past events, as the records of large floods, and using modern techniques of GPS positioning, digital image processing generated by satellites and thematic representation of capping geometry of these floods, we can play in these models events and quantify them with a good accuracy of its effects today. The simulation of these extreme events in a confident base model that available to bring the civil defense prior knowledge of the possible effects of an event this kind, which may be planned escape routes and mitigating actions minimizing loss of life and large economic losses. The same models also serve as analysis impact tool and planning for improvement of the master plan for social development, economic, environmental and research in the academic area. The models presented cover only a small part of the possibility that a work like this enables on research area. Thematic maps with contour lines, medium flood recorded, for environmental conservation area bordering the river and the map of the regions where the extreme event of 41 hit, are available for free use.
Wang, Guang Chao. "Modeling Waves in A Human Brain by Space-Time Conservation Element and Solution Element Method." The Ohio State University, 2011. http://rave.ohiolink.edu/etdc/view?acc_num=osu1313571236.
Full textJusten, Andreas. "A time-space constrained approach for modeling travel and activity patterns." Doctoral thesis, Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, Mathematisch-Naturwissenschaftliche Fakultät II, 2011. http://dx.doi.org/10.18452/16378.
Full textIn this thesis we develop a tour-based approach for modeling activity and travel pattern considering time-space constraints. A hierarchical structure of choice-making builds theoretical background for the model and is based on a set of axiomatic rules. Our central argument is that the time-space constraints can be used for reducing the number of choices and, respectively, control the combinatorics associated with the probabilistic approach. The empirical analysis of our use case, a tour of type ‘Home-Work-SecondaryActivity-Home’, is based on Santiago’s travel survey. In addition, we apply GIS to estimate the so-called search spaces (potential areas where secondary activities are realized) and justify their sizes with the empirical findings. From the data analysis we identify thresholds for the tour-based maximum daily travel times considering a set of mode combinations. We define regimes of starting times and duration of activities depending on socio-economic user groups. The estimation of search spaces is realized considering the time spent at work as well as the distance between the home and work locations. Both criteria were found to be statistically significant. The comparison of modeled results with survey observations allowed concluding that the search spaces are realistic since they capture most of the observed trip destinations. For the estimation of spatial path flows of activities and trips (using SPSS programming language), we define a final choice set of no more than seven alternatives per primary location considering zone-based accessibility and land-use attractiveness. The obtained results support the argument that time-space constraints (daily travel time, search spaces) allow an effective control of combinatorial complexity. Basing on the experience obtained in process of modeling the exemplary tour, the approach can be applied to further tour types offering the possibility to estimate the entire transport demand of Santiago city.
Nguyen, Duc M. "Controllability and Observability of the Discrete Fractional Linear State-Space Model." TopSCHOLAR®, 2018. https://digitalcommons.wku.edu/theses/2574.
Full textGardner, Elvert L. ""Sowing seeds in barren soil" : why space power theory just won't grow /." Maxwell AFB, Ala. : School of Advanced Air and Space Studies, 2008. https://www.afresearch.org/skins/rims/display.aspx?moduleid=be0e99f3-fc56-4ccb-8dfe-670c0822a153&mode=user&action=downloadpaper&objectid=27104bd2-feb9-40b4-87ff-0bc531c869db&rs=PublishedSearch.
Full textVikas, Sharma. "Development of Space-Time Finite Element Method for Seismic Analysis of Hydraulic Structures." Kyoto University, 2018. http://hdl.handle.net/2433/235094.
Full text0048
新制・課程博士
博士(農学)
甲第21374号
農博第2298号
新制||農||1066(附属図書館)
学位論文||H30||N5147(農学部図書室)
京都大学大学院農学研究科地域環境科学専攻
(主査)教授 村上 章, 教授 藤原 正幸, 教授 渦岡 良介
学位規則第4条第1項該当
TUNINETTI, MARTA. "Water footprint assessment in space and time to support local and global sustainability." Doctoral thesis, Politecnico di Torino, 2018. http://hdl.handle.net/11583/2706873.
Full textMeyer, Steven J. "GPS Receiver Testing on the Supersonic Naval Ordnance Research Track (SNORT)." International Foundation for Telemetering, 1997. http://hdl.handle.net/10150/609808.
Full textThere is an interest in using Global Positioning System (GPS) receivers to find: Time Space Position Information (TSPI), miss distances between a missile and target, and using the data real time as an independent tracking aid for range safety. Ashtech, Inc. has several standalone GPS receivers they believe can work at high g levels. This paper investigates how the Ashtech GPS receivers work under high g loading in one axis. The telemetry system used to collect data from the receivers and the reconstruction of the data will also be discussed. The test was done at SNORT (Supersonic Naval Ordnance Research Track) located at NAWS, China Lake, CA. The g level obtained was about +23 g’s with a deceleration of -15 g’s. The velocity reached was about Mach 2.0. A summary of the errors is included.
Sakai, Kotaro. "Seismic Performance Analysis of Fill Dams Using Velocity Based Space-Time Finite Element Method." Doctoral thesis, Kyoto University, 2021. http://hdl.handle.net/2433/263700.
Full textMastalir, Anthony J. "The US response to China's ASAT : an international security space alliance for the future /." Maxwell AFB, Ala. : School of Advanced Air and Space Studies, 2008. https://www.afresearch.org/skins/rims/display.aspx?moduleid=be0e99f3-fc56-4ccb-8dfe-670c0822a153&mode=user&action=downloadpaper&objectid=4b87f6c0-936b-40bf-98d5-f8139a39e139&rs=PublishedSearch.
Full textLochau, Malte [Verfasser]. "Model-based Quality Assurance of Cyber-Physical Systems with Variability in Space, over Time and at Runtime / Malte Lochau." Darmstadt : Universitäts- und Landesbibliothek Darmstadt, 2017. http://d-nb.info/1147968470/34.
Full textFrühwirth-Schnatter, Sylvia. "Applied State Space Modelling of Non-Gaussian Time Series using Integration-based Kalman-filtering." Department of Statistics and Mathematics, WU Vienna University of Economics and Business, 1993. http://epub.wu.ac.at/1558/1/document.pdf.
Full textSeries: Forschungsberichte / Institut für Statistik
Uhl, Philip J. "A Spatio-Temporal Data Model for Zoning." BYU ScholarsArchive, 2002. https://scholarsarchive.byu.edu/etd/1.
Full text






